
The average temperature across the United States (U.S.) has risen at an average rate of 0.16☏ per decade since the beginning of the 20th century, increasing to an even faster rate of 0.31 to 0.54☏ per decade since the 1970s. GHG emissions must also rapidly and significantly be reduced in the near future and eventually eliminated to prevent the increasingly harmful impacts of climate change over the next several decades. People, plants and wildlife, and ecosystems are facing an uncertain future unless adequate actions are taken to adapt to climate change impacts already unfolding and expected to intensify over time. These climate change reports clearly show, based on scientific data, that significant climate change impacts are already occurring. New York's Responding to Climate Change in New York State (ClimAID) report (2011, 2014) (leaves DEC website), the National Climate Assessment (2018) (leaves DEC website), DEC Observed and Projected Climate Change in NYS (PDF), and other climate impact assessment reports show that a variety of climate change impacts have already been observed across the northeastern United States and in New York State. Climate change impacts will continue to worsen as global temperatures and greenhouse gas emissions increase (see Climate Change 101). Higher temperatures, more frequent precipitation and storms, faster rates of ocean warming, and sea level rise are some of the key physical effects of climate change that are impacting communities and ecosystems around the world. The most recent report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (leaves DEC website) states that greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities are responsible for accelerating global warming and climate change.
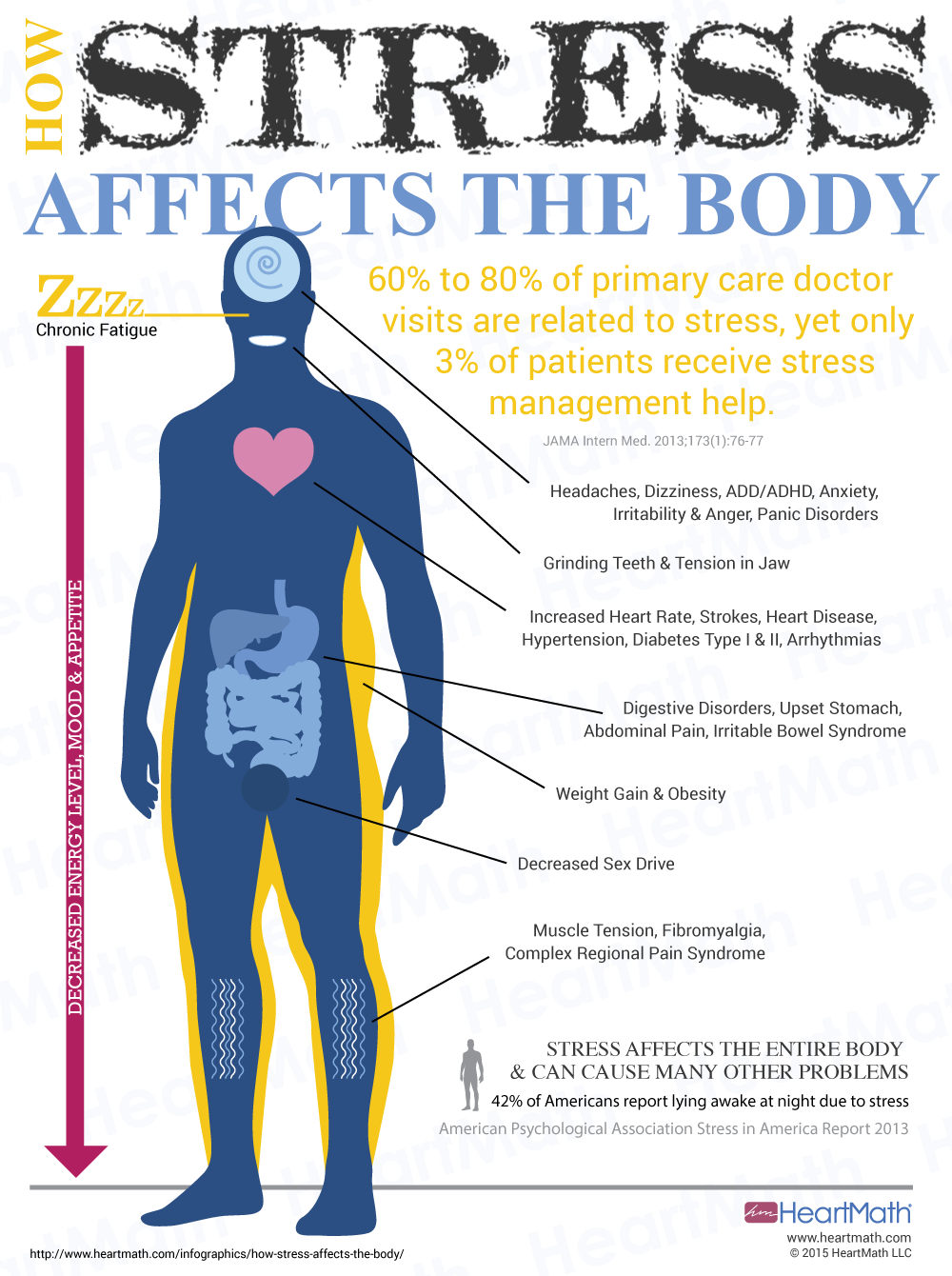
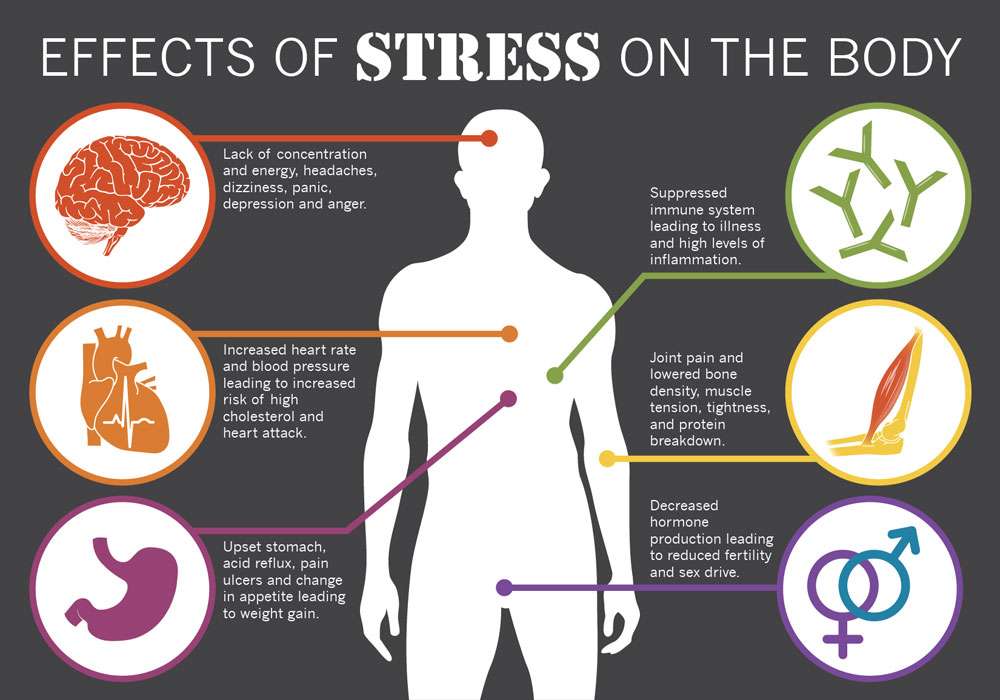


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
